Nice class today with Dr Shamsul Ortho. Syud dengan tak malunya, made a video of kah kian yang malu.. LOLZ.. hope she can put it up here
Showing posts with label Orthopaedic. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Orthopaedic. Show all posts
I'm a bit busy this week. A lot of things to share with u guys.. a bit sad i couldn't share with u guys in this blog.. nway, i'll be in facebook... Sorry guys..

at Dr Vivek trauma seminar

Hip resurfacing surgery offers relief for younger patients. SUZANNA PILLAY finds out how.
A COMMON type of hip arthritis characterised by the progressive wearing away of the cartilage of the afflicted joint, osteoarthritis can be very painful when it increases in severity.
It also affects movement, causing stiff hips, limited range of motion and an awkward gait, amongst other complaints.
“The general rule of thumb that doctors follow when dealing with patients with severe hip arthritis is to recommend total hip replacement (THR) surgery. However, they normally tell patients to wait until after they’re 60 years old, to undergo this surgery.
“THR is not done on the more active and younger patients or on athletes because the wear rates are very high,” said Dr K.
Sivanathan, consultant orthopaedic and arthroplasty surgeon, Tropicana Medical Centre in Petaling Jaya.
This is because in reality, many hip pain sufferers under the age of 60 will outlive a traditional hip replacement and may require additional surgeries (revision hip replacement surgeries) in their lifetime.
He said surgeons were concerned about possible complications that might surface in later revision surgeries because every time it is done, a larger surgery and larger implant had to be used.
Apart from revision surgery, other concerns about THR was the lack of femoral head (thighbone) preservation, reduced range of movements and higher risk of dislocation of implants in more active patients.
“If anybody were to do a THR, we would advise them not to squat or sit in a very low chair, because dislocation can occur. The implant head size is only 28mm in diameter so if you move it beyond a certain angle, the whole thing comes out, as opposed to a normal femoral head which has a higher range of movements.” Instead, younger patients were encouraged to live with their condition as best they could, dulling the pain with anti-inflammatory pain medication, joint supplements like Glucosamine and undergoing physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the hip joint.
But today, the situation is different, thanks to improvements in hip resurfacing surgery implants. Young and active patients don’t have to live with hip pain anymore.
“Hip resurfacing surgery is an advanced surgical procedure for osteoarthritis and hip-related injuries that is suitable for younger or active patients under 60,” said Dr Sivanathan.
“The procedure is a minimally invasive, bone-conserving alternative to conventional total hip replacement because unlike THR, hip resurfacing preserves the head, neck and femur bone. “The femoral head and neck are not removed as in a THR. Instead, the femoral head is reshaped to accept a metal cap placed on the ball of the ball-and-socket hip joint, while the second piece is a cup that forms the socket of the joint. As the hip surfacing implant is made entirely of metal, there is a reduced risk of osteolysis and associated early loosening.” Another plus is that unlike THR, it also made replacement surgery easier. He said if the hip resurfacing implant wears out after 15 years or so, or developed problems, the revision surgery would simply convert it to a standard THR.
However, he said hip resurfacing surgery was not entirely without risk. If the procedure is not done correctly, the femoral neck can break. The person performing it has to be properly trained.
“Also, the hip surfacing implant has to be fitted at the correct angle and care must be taken not to notch the neck when preparing the femoral head to accept the cap.” Dr Sivanathan said patients who undergo hip resurfacing surgery would be given thromboprophylaxis during surgery and shortly after the operation to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT).

“It has been noted that in any surgery involving pelvic fractures, abdominal operations, hip procedures and knee replacements, there is a higher incidence of DVT because the patient would be recumbent in bed for a while.” The issue was highlighted last week (May 11-15), during Thrombosis Awareness Week. It was noted that patients going to hospitals for surgery were at risk from venous thromboembolism (VTE) where blood clots form in the leg veins (DVT), which may then break off and block blood vessels in the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism.
“Deaths from VTE can be minimised through thromboprophylaxis, which is the use of preventive medication, especially in those patients identified as bearing high risk of VTE. These include advanced age, obesity, immobility, pregnancy and past experience with DVT or PE,” said Dr Jamal Azmi Mohamad, consultant orthopaedic and trauma surgeon.
Although exact figures are unavailable, a study conducted in Malaysia among 88 patients who had undergone surgery for total knee replacement, total hip replacement and fracture of the proximal femur with no prophylaxis, found that 55 of them (62.5 per cent) showed evidence of DVT. The prevalence was highest after total knee replacement (76.5 per cent), followed by total hip replacement (64.3 per cent) and lastly, the fracture group (50 per cent).
Dr Jamal, who is also the former president of the Malaysian Orthopaedic Association, said there is a strong need to implement primary prophylaxis to prevent thrombosis, as it is potentially life-saving and more effective than treating complications that may result.

Why me so bother talking about osteoporosis? Because Dr Sajar told so.. muahahaha... Osteoporosis is under group of metabolic bone disorder.
Definition
Osteo - Bone; poro - Pores; osis - condition
Apleys: Can found any.. LoLZ
Stedman: reduction in quality of bone or atropy of skeletal tissue; occurs in postmenopausal women and elderly men, resulting in bone trabeculae that are scanty, thin, and without osteoclastic resorption
Risk factor
Why so important of knowing the risk factor? So we can screen early ler.. Later i will talk how do we screen. Of coz almost all women who are menopause will get this osteoporosis, but if patient got +ve risk factor, it might accelerate the osteoporosis so it's important for us so we can prevent it earlier
Risk Factors are (from apley):
- First Degree family history of Osteoporosis
- Ectomorphic somatotype???
- Hysterectomy done before
- Cigarette Smoking
- Dietary faddism?
WTF is ectomorphic somatotype?? Stupid apley. That's y i never like this book. The book is so simple without explanation.. Hate it so much.. nway.. just forget about it now..
If u are 70 years onwards, additional factors come into play.
- Diminished activities
- Chronic illness
- Dietary deficiency
Basically clinical features depend on which fracture site it occur.
Hip Fracture
Hip fractures are a major cause of loss of independence in older women and men. Overall about half of hip fractures are intertrochanteric and the others are femoral neck fractures. In older women the proportion of trochanteric fractures increases. Trochanteric fractures, but not femoral neck fractures, are related to bone density. Femoral neck fractures, on the other hand, may be more related to mechanical factors. The vast majority of hip fractures occur after a fall. About 5% appear to be "spontaneous" fractures, in which the patient feels a fracture and then falls.
About 60% of women with compression fractures
do not realize they have had a fracture! Vertebral compression fractures vary in degree from mild wedges to complete compression. The symptoms also vary, but the degree of compression is not necessarily related to the amount of pain. It is possible that some of the fractures occurred gradually and therefore did not cause acute pain. When women and men do suffer painful compression fractures, the pain usually lasts from 1 to 2 months, is localized to the back with accompanying muscle spasms, then gradually subsides macam simple muscle strain except lebih lama skit. Usually patients with continuing severe pain should be evaluated for other pathologic etiologies of the fracture, especially malignancy or myeloma. Persistent pain can also be caused by continuing fracture, muscle spasms, spinal stenosis, or degenerative joint disease.
Wrist FractureWrist fractures are more common in women who are 50 to 60 years old. These are caused by falls or other trauma. Osteoporosis does not appear to impair the healing of the wrist fractures, and they cause only short-term disability.
Others such as body shape and consequences
Kyphosis, Heigth loss, Protruding abdomen, decrease pulmonary capacity, reflux esophagitis
Investigations
Xrays
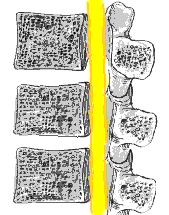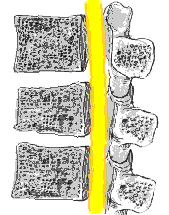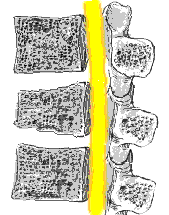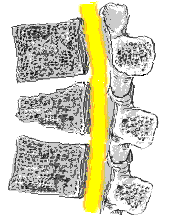
 To correctly interpret a spine xray, it is important to know the definition of a vertebral fracture, which is not quite as straightforward as it first appears. A vertebra can be considered fractured if the anterior height is 80% or less of the posterior height. A new fracture requires loss of at least 20% of anterior or posterior height. See picture on left.
To correctly interpret a spine xray, it is important to know the definition of a vertebral fracture, which is not quite as straightforward as it first appears. A vertebra can be considered fractured if the anterior height is 80% or less of the posterior height. A new fracture requires loss of at least 20% of anterior or posterior height. See picture on left.Xray of the long bones also typically shows an osteoporotic fracture. Usually there is a general reduction in radiographic bone density and abnormal thinning of the cortices. Therefore, here comes DEXA in terms of measuring bone density more accurately
DEXA
For medical student, by knowing what full name of the DEXA is sufficient. No need to know it in detail. Using DEXA is a gold standard to diagnose osteoporosis. It came out in my EOP, 2 years ago, LOLZ. However some centres, DEXA scan were used alot in terms of screening to those with high risk. Now you see the reason why we should know the risk of having it! However it still controversial..haha..
- Dexa scan for those women who have multiple risk factor particularly those with suspected low oestrogen or some other bone-losing disorder, and those who have suffered previous low energy fracture at the menopouse
- Calcium and Vitamin D supplement
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption
- Oestrogen medication (Hormone Replacement Therapy) is the most effective way of maintaining bone density. There was question related to PCM OSCE where we need to advice the patient of having HRT, but the problems about HRT are the complications.
- The newest drugs is Biphosphonates. It is a useful alternative to HRT. Biphosphonates have been shown to prevent bone loss and the to reduce the risk of vertebral and hip fractures.
Managed the fracture first - Internal fixation, rehabilitaion.
Then genaral treatment - Vit D and Calcium supplement, diet with this elements, expose to sunlight, exersice and treatment with Biphosphonates or HRT should also be considered to prevent further loss.
A nice Clinical Practice Guideline you can download here
There is also some Orthopaedic book i like to share. Click here